T-Account: Definition, Example, Recording, and Benefits

If that’s not the case, make sure to double-check your books as you’ve probably made an accounting error along the way. Well, don’t take our word for it – give the software a try out yourself. On February 18th, clients send the $600 worth of invoice payment billed on February 15th.
Company
There’s an increase in the asset Cash and the revenue account, Service Revenue. Angela Boxwell, MAAT, is an accounting and finance expert with over 30 years of experience. She founded Business Accounting Basics, where she provides free advice and resources to small businesses. It will help you understand the total for each side of the T account.
Related AccountingTools Courses
It can be beneficial when you’re making journal entries, which is a way to track all the transactions that have happened in a business. T accounts help people understand how money moves in and out of an account. Each general ledger account will have its own T account, including asset accounts, liabilities, equity, income and expenses. A T-Account is an accounting tool used to track debits and credits for a single account. It is typically represented as two columns with the accounts that have been affected listed on either side, usually labeled Debit (left) and Credit (right). A T-account is a tool used within a ledger to represent a specific account, while a ledger is a complete record of all financial transactions for a company.
Ask Any Financial Question
In this example, the column balances are tallied, so you can understand how the T-accounts work. The account balances are calculated by adding the debit and credit columns together. This sum is typically displayed at the bottom of the corresponding side of the account. Since management uses these ledger accounts, journal entries are posted to the ledger accounts regularly.
- When learning the accounting process, from debits and credits to double-entry, it’s easy to get lost in the process and miss the big picture.
- It’s impossible to provide a complete collection of examples that addresses every financial transaction with the corresponding T account.
- The total difference between the debit and credit columns will be displayed on the bottom of the corresponding side.
- T Accounts allows businesses that use double entry to distinguish easily between those debits and credits.
- Decreases in assets are recorded by credits, so Cash will be credited for $150.
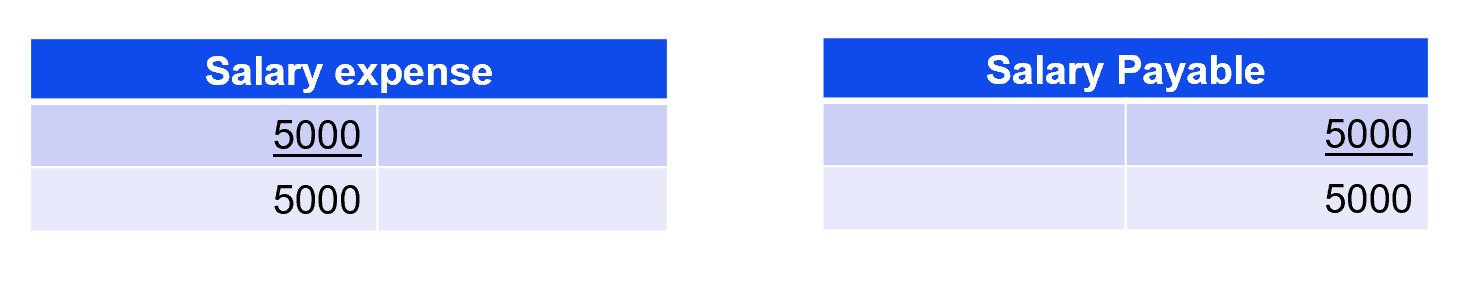
The T-account guides accountants on what to enter in a ledger to get an adjusting balance so that revenues equal expenses. Debits are always posted on the left side of the t account while credits are always posted on the right side. This means that accounts with debit balances like assets will always increase when another debit is added to the account. Likewise, accounts with a credit balance, like liabilities, will always increase when another credit is added to the account.
Expenses decrease the owner’s equity and are recorded as debits, so the Utility Expense account will be debited for $150. Decreases in assets are recorded by credits, so Cash will be credited for $150. A T account is a graphic representation of a general ledger account.
Suppose a business made a cash payment for expenses, then the T accounting would look like this. This prepaid £6000 represents an asset because my landlord owes me 3 months usage of his property since I have paid rent in advance. In this section, I’m going to go through different types of transactions, and I’ll be using T-accounts to display the movement of value through the business.
A T account ledger is an informal way of addressing a double-entry bookkeeping system. On the top, the name of the ledger is mentioned, the left side is for debit entries, and the right side is for credit entries within the ledger. It is essentially a visual or graphical representation of the company’s accounts which can be used to present, scrutinize, or review.
When you enter any forecast activity, the double-entry process is completed for you, saving you time and giving you confidence in the numbers. It really shows how useful it is to try to draw out transactions in T-accounts before they are committed to the company records. In January, I pay £6000 in cash backward inhibitory learning in honeybees to the landlord, so my bank (asset) account is credited £6000. Then, these journal entries are transferred into the general ledger, in the form of T accounts. The ledger is more summarized and brief, in comparison to the journal. Yes, similar to journal entries, T accounts should also always balance.
With that being said, the five most common types of accounts in financial accounting are assets, liabilities, expenses, revenue, and owner’s equity. Because T accounts are posted into the General Ledger of a business, they’re also commonly recognized as ledger accounts. Whenever cash is paid out, the Cash account is credited (and another account is debited). Whenever cash is received, the Cash account is debited (and another account is credited).

Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!